
Basic security and basic pension: Needs-based supplements to the welfare state
29 April 2022
Social assistance benefits are part of a functioning welfare state. It ensures that a citizen in need of assistance is still able to finance his or her necessary livelihood by taking advantage of the appropriate range of benefits. The aim of all state measures is to protect citizens in need and at the same time to prevent such need in the long term (principle of subisidiarity).
In order to achieve this balance of state objectives, we have in the past contributed our expertise and technical elaborations to the political discussion at various points.
Basic security due to indigence
The basic income support scheme is designed to ensure the livelihood of needy people in Germany. This is also intended to prevent hidden and concealed poverty in old age. Basic income support in old age and in the event of reduced earning capacity (§§ 41 ff. SGB XII) is a means-tested social benefit that has existed in Germany since January 1, 2005 to ensure necessary subsistence in the event of need for assistance. In September 2020, there were around 579,000 recipients of basic security in old age.
Basic security in old age and in the event of reduced earning capacity is available to people who are either no longer able to take up gainful employment for reasons of age in order to secure their livelihood, or whose health no longer allows them to do so. It is assumed that there is a higher number of people who would have a claim but do not assert it. The reason for this may be a lack of information about legal rights, but also shame and fear of stigmatization.
People who have reached the age limit or who have reached the age of 18 and are permanently fully incapacitated for work are entitled to this benefit. However, there must be a need.
Basic welfare benefits are calculated on a flat-rate basis and are set by the state governments. Since January 1, 2022, the standard rate has been €449 per month for single persons. Partners and spouses each receive 404 euros.
In addition to this, reasonable expenses for housing and heating are also paid. When an apartment is considered adequate differs depending on the city and the number of people.
Information on basic benefits in old age can be found on the website of the German Pension Insurance (external link).
We played an active role in the reforms of the basic pension system and the adjustment of the recognition of additional income (Riester, company pension plans) by providing content and several example variants, some of which were ultimately adopted in a modified form (see following slide). These continue to provide incentives, particularly for employees with low incomes, to make active provision for old age by ensuring that a certain portion of this additionally generated income is not offset, or only partially offset, against state benefits.
New crediting models – variant 1
After lengthy discussion, the entitlement to a basic pension was introduced as a supplement on January 01, 2021.
Basic pension through lifetime achievement
After a long discussion, the entitlement to a basic pension was introduced as a supplement on January 01, 2021. In most cases, this is a supplement to the previous earned pension if it is not sufficient to cover living expenses.
Possible claims of around 26 million benefit recipients (pensioners, occupationally disabled persons, etc.) are currently being examined by the German Pension Insurance Fund. It is estimated that around 1.3 million people will be entitled to additional benefits. However, there are certain requirements. This includes an income test per household.
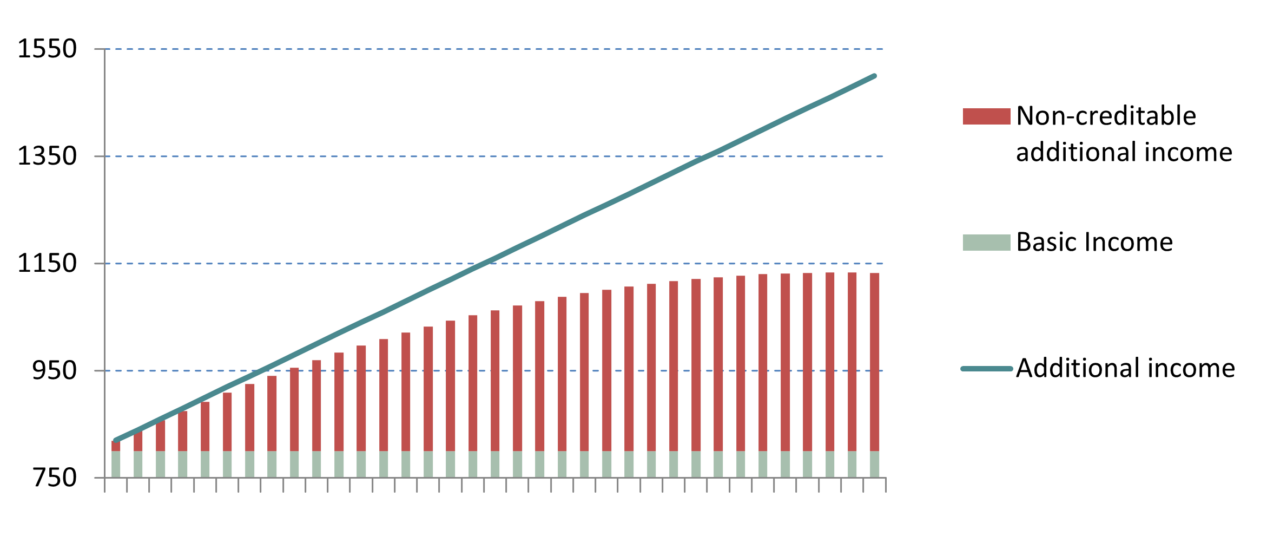
From 33 years of basic pension periods, a partial supplement can be paid, and from 35 years of age, a full supplement, provided that earnings in each contribution year were between 30% and 80% of average earnings. Other periods, such as caring for dependents or years of work abroad, may also count.
The amount of the basic pension can currently be a maximum of about 420 euros. However, a single person may not have more than 1,250 euros and a couple may not have more than 1,950 euros per month in income (e.g., pension payments) when drawing a basic pension. If the amounts are up to 1,600 euros and 2,300 euros, respectively, 60% of the difference and above that amount is fully counted. Incoming pensions and capital gains above the savings allowance are counted towards income. Up to a contribution of 224 euros, basic income support received is not offset.
Information on these topics, among others, is available at: www.deutsche-rentenversicherung.de
The Institute is intensively involved in Germany’s pension system and its reforms. If you would like further information or are interested in the underlying case studies, we would be pleased to hear from you.

